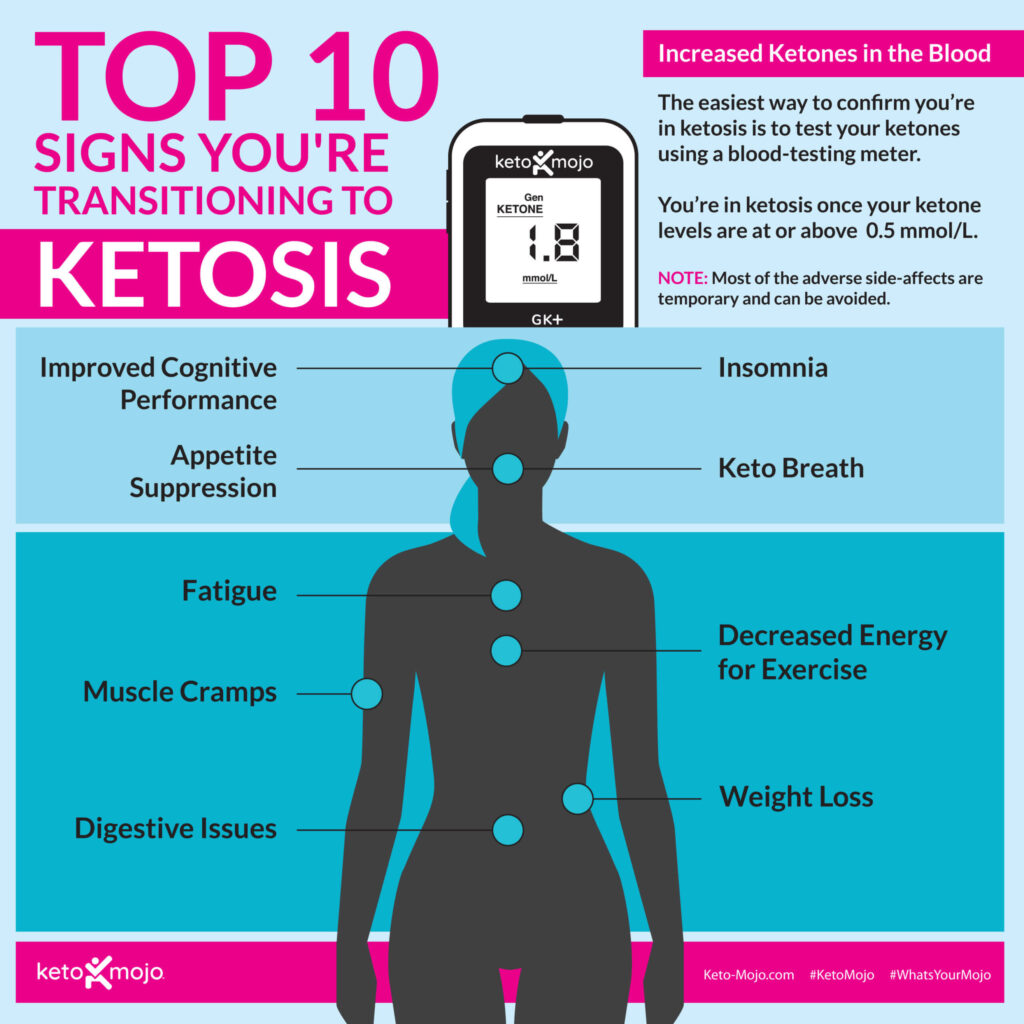
10 Signs and Symptoms of Ketosis
Are you curious about ketosis and its potential benefits? Ketosis occurs when your body switches from burning carbs to burning fat for energy. This can lead to weight loss and improved health. If you’re wondering how to tell if you’re in ketosis, there are 10 signs and symptoms to look out for. These include changes in breath, appetite, and energy levels. Other indicators include increased ketones in the blood, breath, or urine, appetite suppression, increased focus and energy, short-term fatigue, short-term decreases in performance, digestive issues, and insomnia. While it may take some time for your body to adjust to a ketogenic diet, these side effects typically improve over time. Monitoring your ketone levels can also provide a more accurate assessment of ketosis. So, if you’re considering delving into the world of ketosis, keep an eye out for these signs and symptoms to determine if you’re on the right track.
Table of Contents
ToggleSigns and Symptoms of Ketosis
Ketosis is a metabolic state where your body is burning fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. This process occurs when you follow a ketogenic diet, which is a low carb, high fat diet. While this can lead to numerous health benefits, it’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of ketosis. This article will explore the different indicators of ketosis, such as bad breath, weight loss, increased ketones in the blood, breath, or urine, appetite suppression, increased focus and energy, short-term fatigue, short-term decreases in performance, digestive issues, insomnia, and the importance of monitoring ketone levels.
Bad Breath
One common sign of ketosis is bad breath, often described as having a fruity or acetone-like odor. This unpleasant breath is caused by an increased production of ketones in the body. As your body starts burning fat for fuel, it produces ketones as a byproduct. These ketones can be detected in your breath and can result in the distinctive smell.
Cause of Bad Breath in Ketosis
The main cause of bad breath in ketosis is the increased production of ketones. These ketones, specifically acetone, are eliminated from your body through your breath. This can give your breath an unpleasant smell. Additionally, the changes in your diet and the reduction of carbohydrates can also contribute to changes in oral health, which may exacerbate bad breath.
How to Manage Bad Breath
While bad breath can be an unfortunate side effect of ketosis, there are steps you can take to manage it. First and foremost, maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial. Regularly brushing your teeth, flossing, and using mouthwash can help reduce the odor. Staying hydrated can also help flush out ketones from your body and alleviate bad breath. Chewing sugar-free gum or using breath mints can mask the odor temporarily. Finally, if the bad breath persists, it’s advisable to consult your dentist or healthcare provider for further guidance.
Weight Loss
Weight loss is another significant sign of ketosis, making it one of the most sought-after benefits of following a ketogenic diet. When you restrict your carbohydrate intake, your body turns to fat stores for energy. As a result, you may experience steady and noticeable weight loss.
Effect of Ketosis on Weight Loss
Ketosis plays a crucial role in weight loss. By switching your body’s energy source from carbs to fat, you increase fat utilization and decrease fat storage. This can lead to a more efficient fat-burning process and ultimately result in weight loss. Additionally, low carb diets, such as the ketogenic diet, have been shown to reduce appetite and calorie intake, further contributing to weight loss.
Factors Contributing to Weight Loss in Ketosis
Several factors contribute to weight loss in ketosis. One factor is calorie restriction. When following a ketogenic diet, you naturally consume fewer calories due to the elimination of high-carb foods. Another factor is the increase in fat-burning. As your body adapts to using fat for fuel, it becomes more efficient at breaking down and utilizing stored fat. This can lead to significant weight loss over time. Lastly, the reduction in insulin levels that occurs on a ketogenic diet can also play a role in weight loss.
Healthy Weight Loss Strategies during Ketosis
While weight loss is a desired outcome of ketosis, it’s important to approach it in a healthy and sustainable manner. To promote healthy weight loss, focus on consuming nutrient-dense, whole foods. Incorporate a variety of vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet. Practice portion control and avoid excessive calorie intake. Additionally, regular physical activity can complement your ketogenic diet and enhance weight loss. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before beginning any new dietary regimen.
Increased Ketones in the Blood, Breath, or Urine
One of the primary indicators of ketosis is an increase in ketones in the blood, breath, or urine. Ketones are chemical byproducts produced when your body breaks down stored fat for energy. Measuring ketones can help you determine whether you’ve achieved a state of ketosis.
Understanding Ketones
Ketones are produced in the liver as a result of the breakdown of fatty acids. They serve as an alternative fuel source for the body when glucose is limited. The three main types of ketones produced during ketosis are acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB). These ketones can be measured to determine the level of ketosis.
Methods of Measuring Ketones
There are several methods for measuring ketones in your body. One commonly used method is through a blood ketone meter, which measures the concentration of BHB in your blood. Another method is urinary ketone strips, which detect the presence of acetoacetate in your urine. Additionally, breath ketone analyzers are available, measuring the acetone level in your breath. These methods can provide valuable insight into your level of ketosis.
Potential Health Benefits of Increased Ketones
Increased ketone levels have been associated with several health benefits. Ketones have shown promise in reducing inflammation, improving brain function, and enhancing weight loss. Additionally, higher ketone levels are often associated with improved insulin sensitivity, which can be beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome. However, it’s important to note that the health benefits of increased ketones may vary among individuals.
Appetite Suppression
One of the benefits of ketosis is appetite suppression, which can help with weight loss and maintaining a calorie deficit. When your body is in ketosis, you may experience a decrease in appetite, making it easier to adhere to a low calorie diet.
How Ketosis Affects Appetite
The mechanism behind appetite suppression in ketosis is not fully understood but likely involves various factors. The reduction in insulin levels, lower ghrelin (hunger hormone) secretion, and increased production of appetite-suppressing hormones, such as peptide YY (PYY), may contribute to the decreased appetite. Additionally, the consumption of high-fat and protein-rich foods on a ketogenic diet can induce feelings of satiety and fullness.
Benefits of Appetite Suppression in Ketosis
Appetite suppression can be a valuable asset when trying to lose weight or maintain a healthy lifestyle. By reducing your appetite, you may find it easier to stick to a calorie-restricted diet and decrease the likelihood of overeating. This can ultimately lead to a more sustainable and successful weight loss journey.
Managing Hunger in Ketosis
While ketosis may naturally reduce your appetite, it’s important to listen to your body’s hunger cues and consume enough calories for your individual needs. Ensure that you’re eating a well-balanced diet with adequate protein, healthy fats, and low-carb vegetables to promote satiety. Additionally, staying hydrated and incorporating high-fiber foods can help you feel fuller for longer. Experimenting with meal timing and portion sizes can also help manage hunger levels.
Increased Focus and Energy
Another sign of ketosis is increased mental focus and energy. Many individuals report improved cognitive function and higher energy levels when following a ketogenic diet.
Effect of Ketosis on Mental Clarity
When in ketosis, your brain utilizes ketones as a source of energy instead of glucose. This switch in fuel source has been associated with improvements in mental clarity, focus, and cognition. Some people report enhanced productivity and better concentration while in ketosis.
Boosting Energy Levels in Ketosis
Ketosis can provide a steady and sustainable source of energy for your body. By utilizing fat stores for fuel, you avoid the energy crashes associated with high-carb meals. To further boost your energy levels, ensure you’re consuming enough calories and staying properly hydrated. Regular physical activity can also help increase your energy levels and improve overall fitness.
Maintaining Focus and Energy
To maintain focus and energy while in ketosis, it’s vital to prioritize self-care and proper nutrition. Get enough sleep, as inadequate sleep can contribute to mental fatigue. Ensure you’re consuming a well-rounded diet that includes a variety of vitamins and minerals. Consider incorporating natural sources of caffeine, such as coffee or tea, into your routine to enhance alertness. Lastly, managing stress levels through relaxation techniques or mindfulness practices can also support mental clarity and sustained energy.
Short-Term Fatigue
In the early stages of transitioning to a ketogenic diet, it’s common to experience short-term fatigue. This temporary fatigue, often referred to as the “keto flu,” is a result of your body adapting to a new fuel source.
Causes of Fatigue in Ketosis
The initial fatigue experienced during the transition to ketosis can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, your body is adjusting to using fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates, which can temporarily disrupt energy production. Additionally, the reduction in electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, that occurs with the restriction of carbohydrates can contribute to feelings of fatigue. Lastly, inadequate calorie intake or insufficient macronutrient balance can also lead to fatigue.
Overcoming Short-Term Fatigue
While short-term fatigue is a common side effect of transitioning to a ketogenic diet, there are strategies to overcome it. It’s essential to prioritize rest and ensure you’re getting enough sleep. Increase your electrolyte intake by consuming foods rich in sodium, potassium, and magnesium or consider electrolyte supplementation. Gradually reduce your carbohydrate intake to allow your body to adapt more smoothly. Finally, ensure that you’re consuming enough calories and maintaining a balanced macronutrient ratio to support your energy levels.
Short-Term Decreases in Performance
It’s not uncommon to experience short-term decreases in performance when first entering ketosis. This temporary decline in physical or mental performance can be attributed to the body’s adjustment period.
Understanding Performance Changes in Ketosis
The decline in performance during the initial stages of ketosis can be due to various factors. In physical performance, the reduced muscle glycogen stores and the body’s reliance on fat for fuel can lead to a decrease in explosive power and endurance. Similarly, mental performance can be affected as the brain adapts to utilizing ketones instead of glucose. The transition period can result in temporary brain fog or difficulty concentrating.
Strategies to Maintain Performance in Ketosis
While there may be short-term decreases in performance, it’s possible to maintain or even improve performance in ketosis. Gradually implement the ketogenic diet to allow your body to adapt more smoothly. Adequate hydration is crucial, as dehydration can adversely affect performance. Ensure you’re consuming enough calories and maintaining a balanced macronutrient ratio to support your energy needs. Some individuals may benefit from targeted carbohydrate intake before high-intensity workouts to provide a quick energy source. Experiment with your training routine and modify it to suit your energy levels during the adaptation period.
Digestive Issues
Some individuals may experience digestive issues when transitioning to a ketogenic diet. These issues can include constipation, diarrhea, or changes in bowel movements.
Common Digestive Issues in Ketosis
The dietary changes involved in transitioning to a ketogenic diet can impact digestive health. The reduction in high-fiber carbohydrates and an increase in fat intake can lead to changes in bowel movements. Some individuals may experience constipation as the body adjusts to the new eating pattern, while others may have looser stools or diarrhea. These digestive issues are typically temporary and resolve as the body adapts to the diet.
Managing Digestive Issues
To manage digestive issues during the transition to keto, it’s important to prioritize fiber intake. Incorporate low-carb, high-fiber foods, such as vegetables and nuts, into your diet. Stay well hydrated to support bowel regularity. Adequate fat intake is also crucial, as fat helps lubricate the digestive tract. Consider adding sources of healthy fats, such as avocados or olive oil, to your meals. If digestive issues persist or worsen, consult with a healthcare professional for further guidance.
Insomnia
Insomnia, or difficulty staying asleep or falling asleep, can occur during the transition to a ketogenic diet. Changes in energy levels, electrolyte balance, or hormone regulation can contribute to disrupted sleep patterns.
Causes of Insomnia in Ketosis
The causes of insomnia during the adaptation period to ketosis can vary. Firstly, changes in energy levels and increased alertness due to ketones can make it challenging to relax and fall asleep. Electrolyte imbalances, such as decreased sodium or magnesium levels, can also disrupt sleep and lead to restlessness. Additionally, hormonal shifts, particularly changes in insulin and cortisol levels, can affect sleep quality.
Managing Insomnia
To manage insomnia during the transition to ketosis, establish a relaxing bedtime routine. Create a sleep-friendly environment by keeping your bedroom dark, cool, and quiet. Limit caffeine intake, especially in the evening, as it can interfere with sleep. Ensure you’re consuming enough calories and maintaining a balanced macronutrient ratio to support your energy needs throughout the day. Consider supplementing with magnesium, as it has been shown to promote better sleep quality. If insomnia persists, consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
Monitoring Ketone Levels
Monitoring your ketone levels can provide valuable information about your body’s state of ketosis. By regularly assessing your ketone levels, you can determine if you’re reaching and maintaining the desired level of ketosis.
Importance of Monitoring Ketone Levels
Monitoring ketone levels allows you to have a more accurate assessment of your body’s state of ketosis. It helps you determine whether you’re in ketosis, how deep into ketosis you are, and whether any adjustments need to be made to your diet or lifestyle. Monitoring can also serve as motivation and reinforcement of your progress.
Methods of Monitoring Ketones
There are various methods available for monitoring ketone levels. One of the most accurate methods is using a blood ketone meter, which measures the concentration of BHB in your blood. This method requires pricking your finger to collect a blood sample. Urinary ketone strips are another option. These strips detect the presence of acetoacetate in your urine. While affordable and readily available, urinary ketone strips can provide less accurate and delayed results. Breath ketone analyzers, measuring the acetone level in your breath, are also available but may have greater variability.
Interpreting Ketone Levels
Interpreting your ketone levels depends on your goals and individual circumstances. Generally, a blood ketone level of 0.5 mmol/L or higher is indicative of nutritional ketosis. Levels between 1.5-3.0 mmol/L are considered optimal for weight loss and overall health. However, it’s important to note that ketone levels can vary among individuals, and factors such as age, activity levels, and overall health should be taken into account when interpreting results. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to understand the optimal range for your specific needs.
In conclusion, being aware of the signs and symptoms of ketosis is crucial when following a ketogenic diet. Bad breath, weight loss, increased ketones in the blood, breath, or urine, appetite suppression, increased focus and energy, short-term fatigue, short-term decreases in performance, digestive issues, insomnia, and monitoring ketone levels are indicators to watch out for. It’s important to remember that transitioning to a ketogenic diet takes time, and some side effects may occur in the beginning. However, with proper guidance and self-care, many individuals can successfully navigate the adjustments and experience the numerous benefits of ketosis. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure you’re implementing the ketogenic diet safely and effectively for your individual needs.
10 Signs and Symptoms of Ketosis: Learn about the signs and symptoms of ketosis, including bad breath, weight loss, increased ketones, appetite suppression, and more. Discover how to manage these symptoms and achieve the potential benefits of ketosis.