The Role of Selenium in Thyroid Hormone Production and Metabolism
In “The Role of Selenium in Thyroid Hormone Production and Metabolism,” you’ll discover the vital role selenium plays in your body. This essential mineral is responsible for producing thyroid hormones and regulating your metabolism. If you’re looking to improve your thyroid function and aid in weight loss, taking selenium supplements may be beneficial. However, it’s crucial to strike a balance as excessive consumption can lead to toxicity and undesirable side effects like hair loss and nausea. To ensure you receive the right amount, aim for a daily intake of 55 mcg and avoid exceeding 200 mcg through supplements. Alternatively, incorporating high-selenium foods like Brazil nuts, yellowfin tuna, and chicken breast into your diet can be a natural and effective option. Remember, it’s always wise to consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your supplement regimen.
Table of Contents
ToggleThyroid Hormone Production
The importance of thyroid hormones
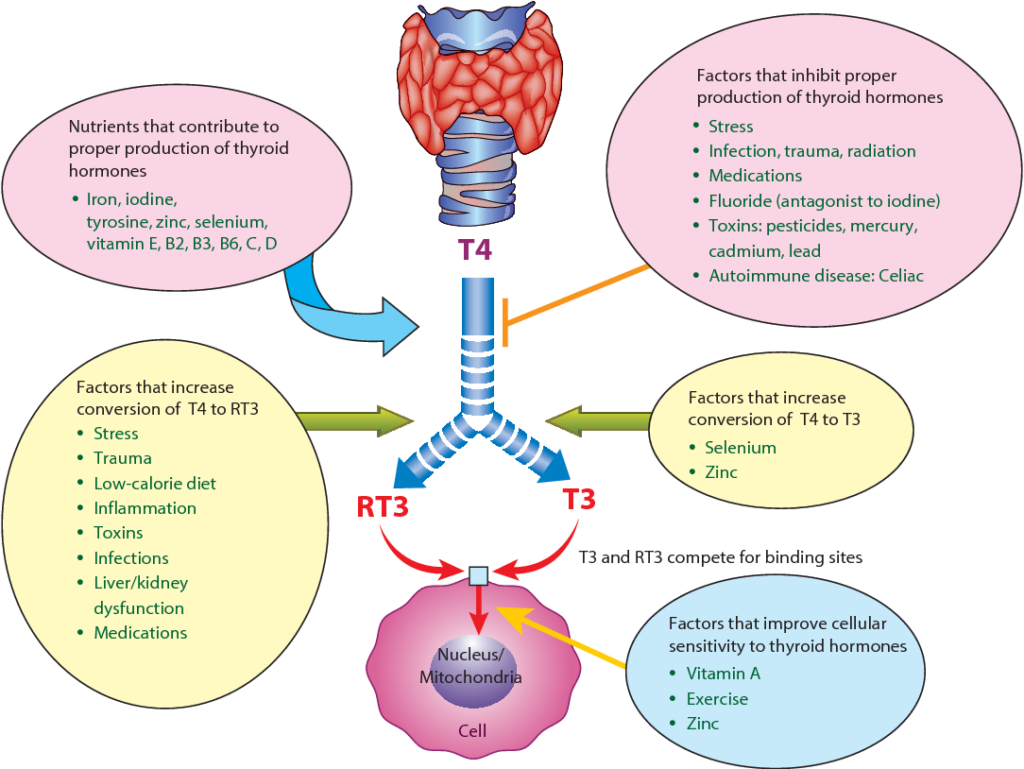
Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes in the body. They are responsible for maintaining metabolism, regulating body temperature, promoting growth and development, and supporting cognitive function. Thyroid hormones also impact heart rate, digestion, muscle control, and many other bodily functions. Without adequate levels of thyroid hormones, these essential processes can become disrupted, leading to a range of health issues.
Thyroid gland and hormone synthesis
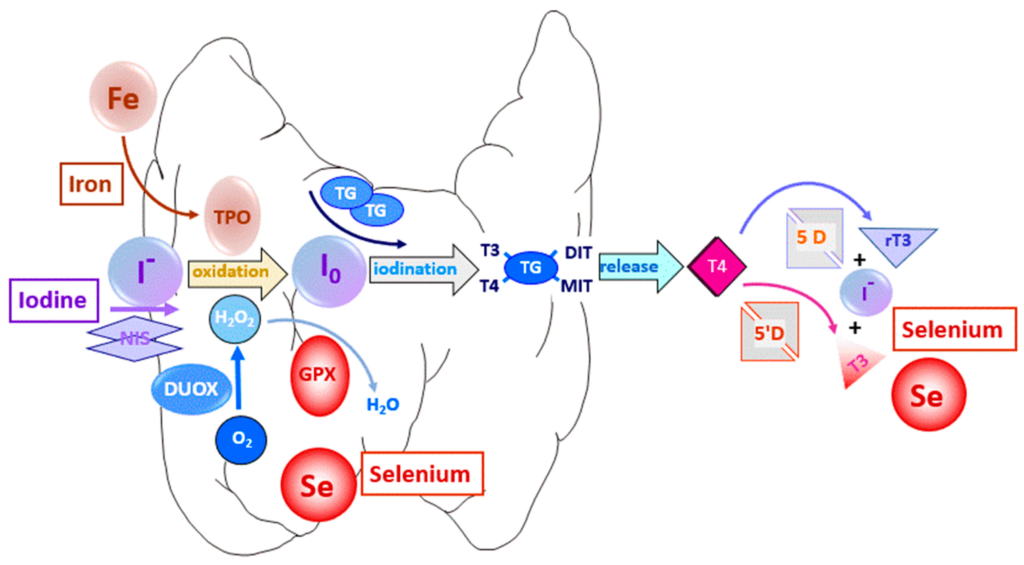
The thyroid gland, located in the front of your neck, is responsible for producing and releasing thyroid hormones. It uses iodine, obtained from the diet, to synthesize thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are then released into the bloodstream, where they travel to various tissues and organs, exerting their effects and maintaining overall physiological balance.
The role of selenium in thyroid hormone production
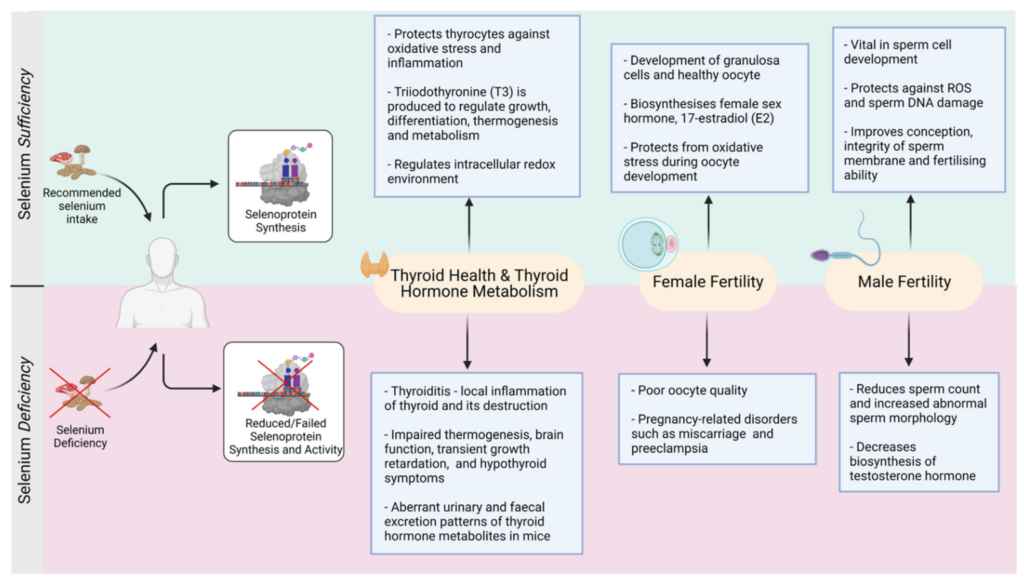
Selenium plays a vital role in thyroid hormone production. It is an essential component of the enzymes involved in converting T4 to the active form of thyroid hormone, T3. These enzymes, known as deiodinases, require selenium as a cofactor to function properly. Without sufficient selenium, the conversion from T4 to T3 may be impaired, resulting in suboptimal levels of active thyroid hormone. Selenium deficiency can, therefore, have a direct impact on thyroid hormone production and overall thyroid function.
Selenium and Metabolism
Basal metabolic rate
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) refers to the number of calories your body needs to perform basic functions while at rest. It accounts for the energy required to maintain vital organs, regulate body temperature, circulate blood, and other essential processes. BMR can vary from person to person, influenced by factors such as age, gender, body composition, and overall health.
Selenium’s impact on metabolism
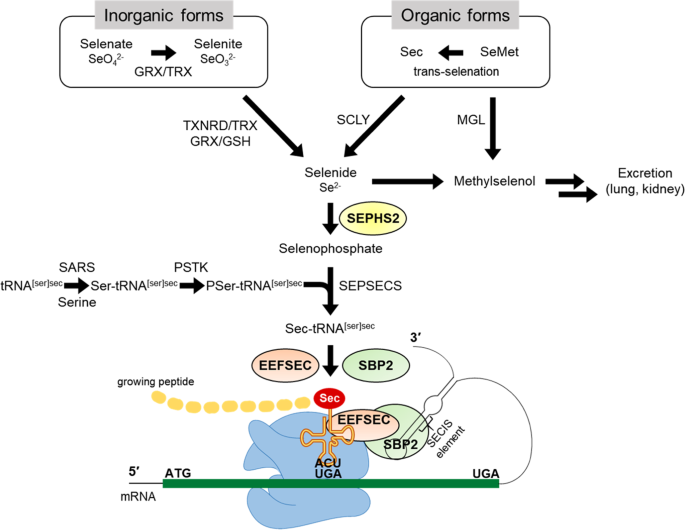
Selenium plays a significant role in regulating metabolism. It is involved in the production of selenoproteins, a group of proteins that have antioxidant properties and are involved in various metabolic processes. These selenoproteins regulate thyroid hormone metabolism, promote energy production from carbohydrates and fats, and contribute to antioxidant defense mechanisms within cells. Adequate selenium levels are, therefore, crucial for maintaining a healthy metabolism and supporting optimal energy production.
The connection between selenium and weight loss
Proper selenium levels may also contribute to healthy weight management. As metabolism plays a vital role in energy expenditure and body weight regulation, any disruption in metabolic processes can impact weight loss or gain. Selenium’s role in thyroid hormone regulation and metabolism provides a link between selenium status and weight management. While selenium alone is not a magic weight loss solution, ensuring adequate selenium levels may support healthy metabolism and optimize the effectiveness of weight loss efforts.
Significance of Selenium
Selenium’s antioxidant properties
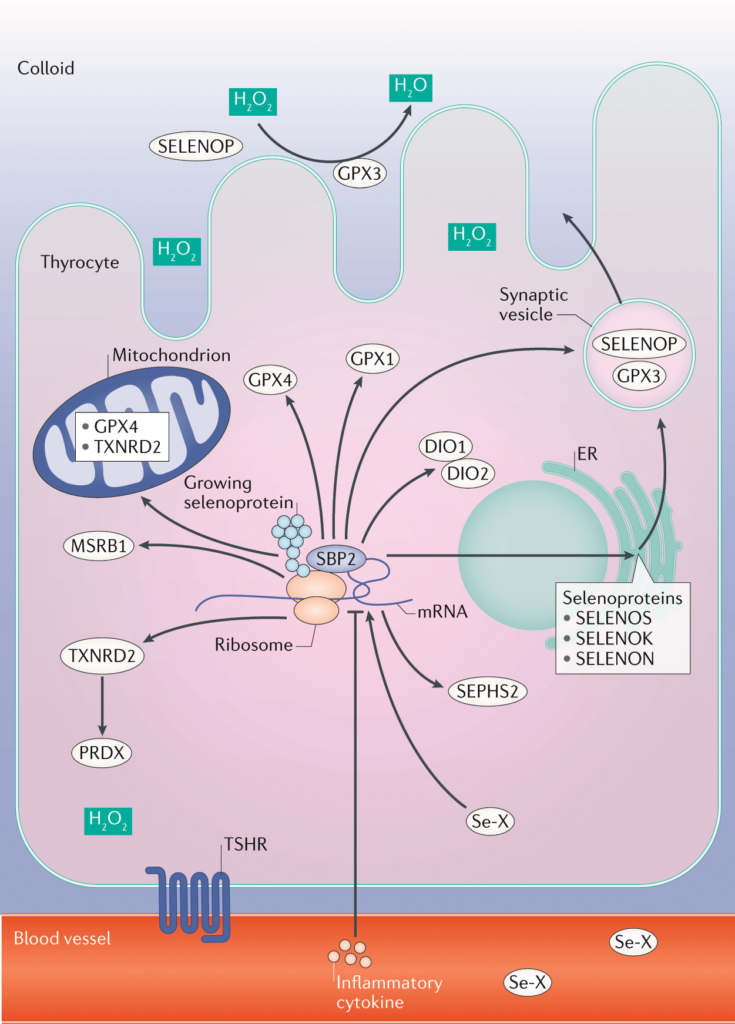
One of the key roles of selenium in the body is its antioxidant activity. Selenium is a necessary component of various antioxidant enzymes, such as glutathione peroxidases and thioredoxin reductases. These enzymes help neutralize harmful free radicals and protect cells from oxidative stress, which can lead to cellular damage and contribute to the development of chronic diseases. By reducing oxidative stress, selenium supports overall health and aids in the prevention of conditions related to oxidative damage.
Immune function and selenium
Selenium plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy immune system. Adequate selenium levels are required for the proper functioning of immune cells and the production of cytokines, which are proteins involved in cell signaling during immune responses. Research has shown that selenium deficiency can impair immune function and increase susceptibility to infections. On the other hand, maintaining optimal selenium levels can enhance immune responses, support immune cell function, and aid in maintaining overall immune system health.
Selenium and thyroid health
Thyroid health is closely linked to selenium status. As mentioned earlier, selenium is essential for the synthesis and conversion of thyroid hormones. It is also involved in protecting the thyroid gland from oxidative damage. Selenium’s antioxidant properties help maintain the integrity of thyroid cells and protect them from free radicals that can damage the gland. Ensuring an adequate intake of selenium is crucial for optimal thyroid function and overall thyroid health.
Selenium Deficiency and Thyroid Dysfunction
Common signs of selenium deficiency
Selenium deficiency can manifest in various ways, and its symptoms may overlap with other health conditions. Some common signs of selenium deficiency include fatigue, weakness, muscle pain, joint discomfort, hair loss, changes in skin and nails, and impaired cognitive function. These symptoms can be indicative of disrupted thyroid function, as selenium deficiency can lead to impaired synthesis and conversion of thyroid hormones.
Impact of selenium deficiency on thyroid
Selenium deficiency can have a direct impact on the thyroid gland and its ability to produce and release thyroid hormones. Without sufficient selenium, the activity of deiodinase enzymes, crucial for the conversion of T4 to T3, can be compromised. This can result in reduced levels of active thyroid hormone, leading to hypothyroidism or an underactive thyroid. Hypothyroidism is associated with symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, constipation, dry skin, and cognitive impairment.
The link between selenium deficiency and thyroid diseases
Selenium deficiency has been linked to various thyroid diseases. One such condition is autoimmune thyroiditis, which includes Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. These autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland. Research suggests that selenium supplementation may have beneficial effects in reducing thyroid antibody levels and improving thyroid function in individuals with autoimmune thyroiditis. However, further studies are still needed to fully understand the relationship between selenium deficiency and thyroid diseases.
Selenium Supplementation
Benefits of selenium supplementation
Selenium supplementation can provide several benefits, particularly for individuals with low selenium levels or those at risk of deficiency. By ensuring adequate selenium intake, supplementation can support thyroid hormone production, maintain optimal metabolism, and support overall thyroid health. Selenium’s antioxidant properties also make it beneficial for immune system function and protection against oxidative stress. Additionally, selenium supplementation may be beneficial for individuals with thyroid disorders, as it has shown potential in reducing thyroid antibody levels in autoimmune thyroiditis.
Appropriate dosage of selenium supplements
The recommended daily intake of selenium for adults is 55 mcg. It is important not to exceed the tolerable upper intake level (UL) of 200 mcg for adults, as excessive selenium intake can lead to toxicity. When considering selenium supplementation, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who can assess your specific needs and determine the appropriate dosage for you. Individual requirements may vary depending on age, sex, overall health, and any underlying medical conditions.
Potential side effects and risks of excessive selenium intake
While selenium is essential for overall health, excessive intake can have adverse effects. Consuming too much selenium from supplements can lead to selenium toxicity, also known as selenosis. Symptoms of selenosis include gastrointestinal problems, hair loss, nail brittleness, skin lesions, nerve damage, and even respiratory difficulties. It is important to follow the recommended dosage guidelines and avoid exceeding the tolerable upper intake level to minimize the risk of selenium-related side effects.
Selenium-Rich Foods
Brazil nuts: A top source of selenium
Brazil nuts are a fantastic source of selenium, making them a top choice for individuals looking to increase their selenium intake through food sources. Just one Brazil nut can provide more than one hundred percent of your daily selenium needs. Incorporating a couple of Brazil nuts into your daily diet can help ensure you are meeting your selenium requirements. However, it is important not to consume too many Brazil nuts as excessive selenium intake can be harmful. A few Brazil nuts a day can provide the selenium your body needs without overwhelming your system.
Other selenium-rich foods
In addition to Brazil nuts, there are other food sources that can help increase your selenium intake. These include seafood such as yellowfin tuna, sardines, and shrimp, as well as poultry like chicken and turkey. Other options include eggs, whole grains, spinach, and mushrooms. By diversifying your diet and incorporating these selenium-rich foods, you can support your body’s selenium needs and maintain overall health.
Dietary recommendations for selenium intake
The recommended daily intake of selenium can be met through a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of selenium-rich foods. For most individuals, consuming two to three servings of seafood per week and incorporating sources like Brazil nuts and other selenium-rich foods into daily meals is sufficient to meet the recommended daily selenium intake of 55 mcg. However, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure your dietary choices align with your specific needs and health goals.
Selenium and Thyroid Disorders
Selenium’s role in Graves’ disease
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder characterized by an overactive thyroid gland. Research suggests that selenium supplementation may have potential benefits for individuals with Graves’ disease. Several studies have shown that selenium supplementation, in conjunction with standard treatment, can improve thyroid function and reduce the severity of symptoms associated with Graves’ disease. Selenium’s role in reducing thyroid antibody levels and modulating immune responses may contribute to its beneficial effects in individuals with this thyroid disorder.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and selenium
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition that results in an underactive thyroid gland. While selenium deficiency has been linked to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, its supplementation has shown promising results in reducing thyroid antibody levels and improving thyroid function. Selenium’s antioxidant properties and its role in immune regulation make it an attractive option for individuals with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and optimal dosages of selenium supplementation for this specific condition.
Selenium’s potential impact on thyroid nodules
Thyroid nodules are small growths or lumps that develop within the thyroid gland. While most nodules are non-cancerous and benign, they can sometimes interfere with thyroid function. Research suggests that selenium supplementation may have potential benefits in reducing the growth and progression of thyroid nodules. Selenium’s antioxidant properties and its ability to modulate immune responses may help reduce inflammation and promote the health of thyroid cells. However, further studies are needed to establish definitive recommendations for selenium supplementation in individuals with thyroid nodules.
Interactions of Selenium with Other Nutrients
Iodine and selenium synergy
Iodine and selenium work synergistically in thyroid hormone production and overall thyroid function. Adequate levels of both minerals are necessary for optimal thyroid health. Iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones, while selenium is essential for their activation and metabolism. Having adequate levels of both nutrients ensures the proper functioning of the thyroid gland and the production of sufficient thyroid hormones. It is important to maintain a balanced intake of iodine and selenium to support optimal thyroid function.
Vitamin E and selenium
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin with antioxidant properties. It works together with selenium to enhance antioxidant defenses and protect cells from oxidative damage. Selenium is necessary for the production of selenoproteins, including glutathione peroxidase, which is involved in neutralizing free radicals. Vitamin E helps regenerate this enzyme, allowing it to continue its role in protecting cells. The combination of selenium and vitamin E can have a synergistic effect on overall antioxidant capacity and health.
Zinc and selenium interaction
Zinc and selenium interact in several metabolic processes, including immune function and antioxidant defense. Both minerals play essential roles in supporting a healthy immune response and maintaining overall immune system function. Additionally, zinc is involved in the activation of selenoproteins, such as glutathione peroxidase, which require selenium to function properly. Adequate levels of both zinc and selenium are crucial for optimal immune function and general health.
Research and Evidence
Studies on selenium and thyroid function
Numerous studies have investigated the relationship between selenium and thyroid function. Research has shown that selenium supplementation can improve thyroid hormone levels, reduce thyroid antibody levels, and enhance overall thyroid function. These studies have primarily focused on individuals with thyroid disorders, such as autoimmune thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. However, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms by which selenium affects thyroid function and to establish clear guidelines for selenium supplementation.
Clinical trials and selenium supplementation
Clinical trials have been conducted to assess the effects of selenium supplementation on various aspects of health, including thyroid function. Some trials have shown positive outcomes, indicating the potential benefits of selenium supplementation for individuals with thyroid disorders. These trials have evaluated selenium’s impact on thyroid hormone levels, thyroid antibody levels, and symptom severity. While the results are promising, further research is needed to confirm these findings and provide more precise recommendations for selenium supplementation.
Conflicting research and further investigation
While some studies have shown positive effects of selenium supplementation on thyroid function, there is still conflicting evidence in the research. Some studies have shown no significant improvement in thyroid parameters with selenium supplementation. These conflicting results suggest that the relationship between selenium and thyroid function is complex and may depend on various factors such as baseline selenium status, the presence of thyroid disorders, and individual variations. Further investigation is necessary to fully understand the role of selenium in thyroid function and its potential benefits.
Guidelines for Selenium Supplementation
Consulting a healthcare professional
Before starting any supplement regimen, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess your individual needs, review your medical history, and help you determine whether selenium supplementation is necessary or beneficial for you. They can also guide you in selecting the appropriate dosage and monitor your progress to ensure optimal health outcomes.
Recommended daily intake of selenium
The recommended daily intake of selenium for adults is 55 mcg. This intake is typically achievable through a balanced diet that includes selenium-rich foods. However, individual requirements may vary, especially for individuals with specific health conditions or nutritional needs. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine your specific selenium needs and ensure you are meeting the recommended daily intake.
Safe and responsible selenium supplementation practices
If selenium supplementation is deemed necessary, it is important to follow safe and responsible practices. Start with the lowest effective dose recommended by your healthcare professional and monitor your response to the supplement. Never exceed the tolerable upper intake level of 200 mcg per day to avoid selenium toxicity. Regularly reassess your selenium status and adjust supplementation as necessary under the guidance of your healthcare professional. Remember, supplements should complement a healthy diet and should not substitute for a varied and balanced eating plan.
In conclusion, selenium plays a vital role in thyroid hormone production, metabolism, and overall health. Ensuring optimal selenium levels through a well-balanced diet or appropriate supplementation can support thyroid function, maintain a healthy metabolism, and enhance immune system function. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine your individual selenium needs and ensure safe and responsible supplementation practices. By incorporating selenium-rich foods into your daily meals and following professional guidance, you can support your thyroid health and overall well-being.
Discover the vital role selenium plays in thyroid hormone production and metabolism. Learn how to improve thyroid function and metabolism with selenium supplements and high-selenium foods. Avoid toxicity and side effects with proper dosage and consult a healthcare professional.