Understanding the Ketosis Process: Converting Fat into Ketones for Energy
In “Understanding the Ketosis Process: Converting Fat into Ketones for Energy,” you’ll discover the fascinating metabolic process of ketosis, where the body converts fat into ketones for energy. This article will delve into the benefits of ketosis, such as weight loss, managing type 2 diabetes, and addressing neurological disorders. To embark on this journey, you’ll need to minimize carb consumption, incorporate coconut oil into your diet, increase physical activity, and boost your healthy fat intake. The article also explores the role of fasting, maintaining protein intake, and preserving muscle mass during a low carb ketogenic diet. Join us as we explore this exciting process of harnessing fat for energy and unlocking its potential for a healthier you!
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Ketosis Process
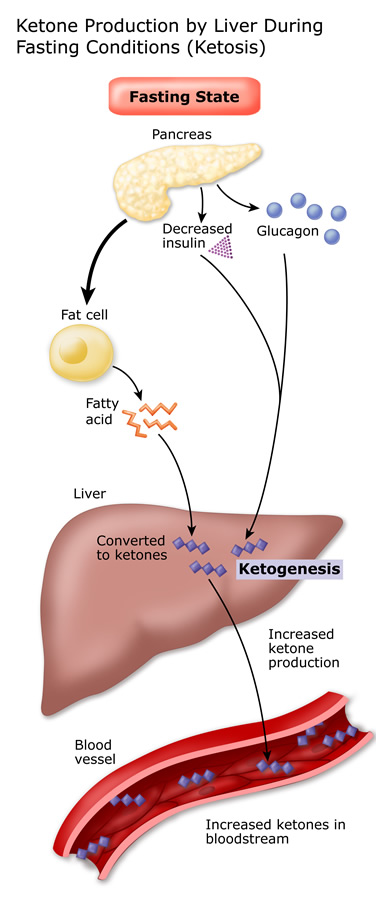
Ketosis is a metabolic process in which the body converts fat into ketones for energy. This occurs when the body is in a state of low carbohydrate intake, forcing it to use fat as its primary source of fuel instead of carbohydrates. The ketones produced during this process can provide a steady and sustainable source of energy for the body.
Definition of Ketosis
Ketosis is a natural process that occurs when the body doesn’t have enough carbohydrates to burn for energy. In response, it starts breaking down fat stored in the body to produce ketones, which are then used as an alternative fuel source. This metabolic state is referred to as ketosis.
How Ketosis Works
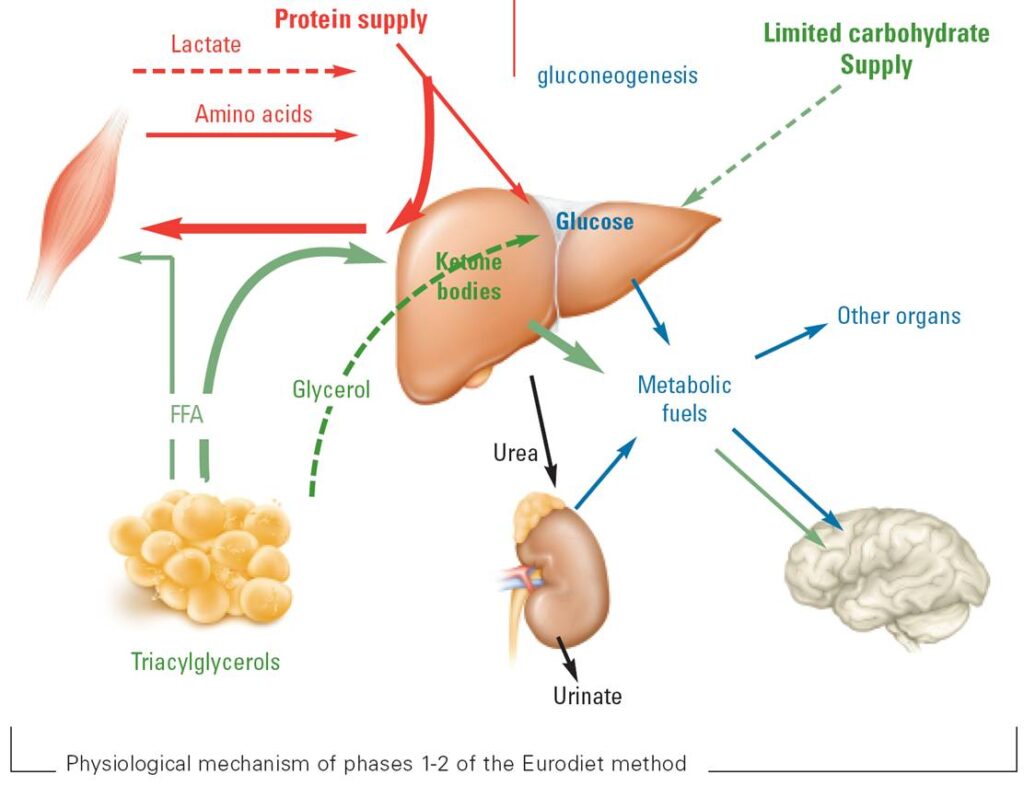
When you eat a low-carb or ketogenic diet, your body starts to deplete its glycogen stores, which are the stored form of carbohydrates. As glycogen levels decrease, insulin levels drop, and the body begins to release fatty acids from fat stores. These fatty acids are then transported to the liver, where they are broken down into ketone bodies. These ketone bodies, such as acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone, can be used by the brain and other organs as a source of energy.
Benefits of Ketosis
Ketosis has several benefits for overall health and well-being. One of the most well-known benefits is weight loss. Due to the increased fat burning and reduced appetite associated with ketosis, many individuals experience significant weight loss while following a ketogenic diet.
Ketosis also has positive effects on blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity, making it beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance. By reducing carbohydrate intake and relying on ketones for energy, individuals with diabetes can better regulate their blood sugar levels and improve their overall metabolic health.
Moreover, ketosis has shown promise in the treatment of neurological disorders such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. The brain can effectively utilize ketones as an energy source, providing neuroprotective benefits and potentially improving cognitive function.
Entering Ketosis
Entering ketosis requires specific dietary and lifestyle modifications. By following these strategies, you can shift your body into a state of ketosis and experience the many benefits it offers.
Minimizing Carb Consumption
The first step to entering ketosis is minimizing your carbohydrate consumption. This means significantly reducing your intake of foods that are high in carbohydrates, such as grains, legumes, starchy vegetables, and sugary foods. Instead, focus on consuming foods that are low in carbs but high in healthy fats and protein.
Including Coconut Oil in Diet
Incorporating coconut oil into your diet can greatly aid in the process of entering ketosis. Coconut oil contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are easily converted into ketones by the liver. Adding coconut oil to your meals or using it as a cooking oil can provide a quick and efficient source of ketones.
Increasing Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can help accelerate the process of entering ketosis. When you exercise, your body depletes glycogen stores and increases the demand for energy. By incorporating both aerobic and resistance training exercises into your routine, you can enhance the production and utilization of ketones.
Increasing Healthy Fat Intake
To enter and maintain ketosis, it is crucial to increase your intake of healthy fats. These fats serve as a primary energy source and support the production of ketone bodies. Include foods such as avocados, nuts and seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish in your diet to boost your healthy fat intake.
Trying Fasting or Fat Fast
Fasting or engaging in a fat fast can provide a jumpstart to ketosis. Fasting involves abstaining from food for a specific period, while a fat fast involves consuming primarily healthy fats and minimal protein and carbohydrates. Both methods help deplete glycogen stores and force the body to rely on fat for fuel, leading to the production of ketones.
Maintaining Adequate Protein Intake
While it’s important to reduce carbohydrate intake, it’s equally important to maintain adequate protein intake during ketosis. Protein is essential for maintaining muscle mass and supporting various bodily functions. Aim for a moderate protein intake, typically around 0.6-1.0 grams of protein per pound of lean body mass.
Carb Consumption for Ketosis
To sustain ketosis, it’s important to monitor and restrict your carbohydrate consumption. Here’s what you need to know about carb intake for ketosis.
Recommended Net Carb Intake for Ketosis
In general, consuming 20-50 grams of net carbs per day is recommended for achieving and maintaining ketosis. Net carbs are calculated by subtracting the fiber content from the total carbohydrate content of a food. By keeping net carbs low, you can ensure that your body remains in a state of ketosis.
Effects of Carbohydrate Restriction on Ketosis
Restricting carbohydrate intake is essential for achieving and maintaining ketosis. By limiting carbohydrates, your body is forced to rely on fat for fuel, leading to the production of ketones. As a result, blood ketone levels increase, and your body enters a state of nutritional ketosis.
Carb Sources to Avoid
To successfully enter and maintain ketosis, it’s important to avoid certain carb sources that can quickly kick you out of ketosis. Foods that are high in refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pasta, desserts, and sugary beverages, should be avoided. Instead, focus on consuming non-starchy vegetables, low-sugar fruits, and healthy fats.
Coconut Oil and Ketosis
Coconut oil is a valuable asset when it comes to entering and maintaining ketosis. Here’s why it plays a crucial role in the process.
Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCTs)
Coconut oil contains a unique type of fat known as medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs). Unlike long-chain fatty acids found in most fats, MCTs are rapidly absorbed and transported directly to the liver. MCTs provide a quick source of energy and can be easily converted into ketones.
Conversion of MCTs into Ketones
When you consume coconut oil rich in MCTs, your liver rapidly metabolizes these fats into ketones. This rapid conversion allows for an immediate supply of ketones to fuel your body and brain. As a result, coconut oil can enhance the production of ketones and facilitate the transition into ketosis.
Benefits of Coconut Oil for Ketosis
Incorporating coconut oil into your diet not only aids in the process of entering ketosis but also offers additional benefits. Coconut oil has been shown to boost metabolism, reduce appetite, and promote fat burning. Additionally, the MCTs in coconut oil have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, supporting overall health and well-being.
Physical Activity and Ketone Production
Engaging in regular physical activity can significantly affect ketone production and enhance the benefits of ketosis. Here’s why exercise is crucial for ketosis.
Effects of Physical Activity on Ketosis
Physical activity can have a positive impact on ketosis. When you exercise, your body uses stored glycogen for energy. As glycogen levels deplete, the body starts to rely on fat as its primary fuel source, leading to increased ketone production. Regular exercise can help deplete glycogen stores and promote further fat metabolism.
Increasing Ketone Production through Exercise
Various studies have shown that aerobic exercise, such as walking, cycling, or jogging, can increase ketone production. When you engage in aerobic activities, your body requires more energy, prompting greater fat burning and ketone production. Resistance training, such as weightlifting, can also benefit ketosis by preserving muscle mass and supporting metabolic health.
Recommended Types of Physical Activity
To maximize the benefits of ketosis, it’s recommended to engage in a combination of aerobic and resistance training exercises. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week, or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity. Additionally, incorporate two or more days of resistance training to build and maintain muscle mass.
High-Fat Diet for Ketosis
A high-fat diet is a key component of a successful ketogenic lifestyle. Here’s why a high-fat diet is beneficial for ketosis.
Calorie Distribution in a High-Fat Diet
In a high-fat diet for ketosis, approximately 60-80% of calories should come from fat. This high fat intake is necessary to provide the body with an alternative source of energy in the absence of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates should be limited to around 5-10% of calories, while protein intake should be moderate at around 20-30% of calories.
Benefits of High-Fat Diet for Ketone Levels
Consuming a high-fat diet promotes the production and utilization of ketones for energy. By maximizing fat intake, the body is constantly supplied with fatty acids, which are converted into ketones. This increases blood ketone levels and maintains ketosis, enabling the body to burn fat efficiently.
Recommended Sources of Healthy Fats
When following a high-fat diet for ketosis, it’s important to choose healthy sources of fats. Include foods such as avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, nuts and seeds, fatty fish, and grass-fed butter or ghee. These fats are nutrient-dense and provide essential fatty acids, while also promoting satiety and overall well-being.
Fasting and Ketosis
Fasting is a powerful tool that can be used to induce and maintain ketosis. Here’s how fasting can benefit your journey into ketosis.
Inducing Ketosis through Fasting
Fasting involves abstaining from food for a specific period, typically for at least 16 hours or up to 24-48 hours. During fasting, the body depletes glycogen stores and starts utilizing stored fat as its primary energy source. This leads to the production of ketones and the induction of ketosis.
Intermittent Fasting and Ketone Production
Intermittent fasting is a popular approach to fasting that involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. This pattern of eating can increase ketone production and improve insulin sensitivity. By restricting your eating window and incorporating intermittent fasting into your routine, you can optimize ketone production and support overall health.
Benefits and Risks of Fasting for Ketosis
Fasting can provide numerous benefits for ketosis, including enhanced fat burning, increased autophagy (cellular repair), improved insulin sensitivity, and potential weight loss. However, fasting may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with underlying health conditions. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before attempting any prolonged fasting protocols.
Adequate Protein Intake for Ketosis
Protein is an essential macronutrient that plays a crucial role in a ketogenic diet. Here’s why adequate protein intake is important for ketosis.
Importance of Protein in Ketogenic Diet
Protein is necessary for numerous functions in the body, including muscle maintenance, tissue repair, and the production of enzymes and hormones. In a ketogenic diet, protein also helps support satiety and preserve lean muscle mass. However, excessive protein intake can hinder ketosis by being converted into glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis.
Recommended Protein Intake
To maintain ketosis while preserving muscle mass, it’s recommended to consume a moderate amount of protein. Aim for approximately 0.6-1.0 grams of protein per pound of lean body mass. This amount should be spread evenly throughout the day and derived from high-quality sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and plant-based proteins.
Sources of Protein for Ketosis
When selecting protein sources for a ketogenic diet, choose those that are low in carbohydrates and processed additives. Opt for lean cuts of meat, wild-caught fish, free-range poultry, whole eggs, and plant-based proteins such as tempeh or tofu. These protein sources will provide the necessary amino acids without compromising ketosis.
Maintaining Muscle Mass on Ketogenic Diet
Preserving muscle mass is essential during a low-carb ketogenic diet. Here’s why muscle maintenance matters and how to prevent muscle loss in ketosis.
Role of Muscle Mass in Ketosis
Maintaining muscle mass while following a ketogenic diet is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, lean muscle mass contributes to overall strength, mobility, and physical performance. Additionally, muscle tissue is metabolically active and helps maximize calorie burn, even at rest. Finally, preserving muscle mass can prevent a decrease in metabolic rate, which can occur during weight loss.
Preventing Muscle Loss in Ketosis
To prevent muscle loss while in ketosis, it’s important to combine regular resistance training with an adequate protein intake. Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, stimulates muscle protein synthesis and helps preserve muscle mass. Additionally, ensuring that you consume enough protein will provide the necessary amino acids for muscle repair and growth.
Recommended Strategies for Muscle Maintenance
To maintain muscle mass while on a ketogenic diet, consider the following strategies:
- Incorporate resistance training: Engage in strength-focused exercises at least two to three times per week to stimulate muscle growth and preservation.
- Consume sufficient protein: Aim for an adequate protein intake to support muscle repair and growth. Spread your protein intake evenly throughout the day to optimize muscle protein synthesis.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration is crucial for muscle health and function. Drink enough water throughout the day to support optimal muscle function.
- Prioritize sleep: Quality sleep is essential for muscle recovery and growth. Aim for seven to nine hours of uninterrupted sleep each night.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact muscle maintenance. Incorporate stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing into your daily routine.
Conclusion
The process of ketosis offers numerous benefits for weight loss, type 2 diabetes management, and neurological health. By implementing strategies such as minimizing carb consumption, including coconut oil in your diet, increasing physical activity, increasing healthy fat intake, trying fasting or fat fasting, and maintaining adequate protein intake, you can successfully enter and maintain ketosis.
It’s important to remember that ketosis is not appropriate for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions or specific dietary needs. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making any drastic dietary changes.
In summary, the key to understanding and implementing ketosis lies in a balanced approach that considers individual needs and preferences. With proper planning, education, and guidance, you can harness the benefits of ketosis and optimize your overall health and well-being.
Learn about the fascinating process of ketosis, where the body converts fat into ketones for energy. Discover the benefits, including weight loss and managing type 2 diabetes. Find out how to enter ketosis by minimizing carb consumption, incorporating coconut oil, increasing physical activity, and boosting healthy fat intake. Explore the role of fasting and maintaining protein intake. Join us on this exciting journey of harnessing fat for energy and unlocking a healthier you!