Intermittent Fasting: A Beginner’s Guide To Time-Restricted Eating
Have you ever heard of intermittent fasting? It’s a trendy eating pattern that has gained popularity in recent years. So, what exactly is it? Well, in a nutshell, intermittent fasting is an eating pattern that involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. It’s not a diet, per se, but rather a way of eating that can have some pretty amazing health benefits. In this article, we’ll dive into the details of intermittent fasting and explore how it can help you improve your overall health and achieve your weight loss goals.
So now that you know what intermittent fasting is, let’s talk about how it actually works. The most common method of intermittent fasting is known as time-restricted eating, which involves limiting your eating window to a certain number of hours each day. For example, you might choose to only eat between the hours of 12 pm and 8 pm, giving yourself a 16-hour fasting period overnight. During the fasting period, you’re allowed to drink water, tea, or coffee (without sugar or cream) to help keep you satisfied.
Now, you might be wondering why on earth anyone would willingly choose to skip meals and go without food for extended periods of time. Well, besides the potential for weight loss, intermittent fasting has been shown to have numerous other health benefits. Research has found that it can improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce inflammation in the body. It may also help boost brain health and improve cognitive function. Plus, some people find that intermittent fasting can be a more sustainable way of eating, compared to traditional calorie-restricted diets.
Interested in giving intermittent fasting a try? Stay tuned for our upcoming article where we’ll discuss the different methods of intermittent fasting, provide tips for getting started, and address some common concerns and misconceptions. Whether you’re hoping to shed a few pounds, improve your overall health, or just shake up your eating routine, intermittent fasting could be an excellent strategy to consider.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Intermittent Fasting?
Definition and explanation of intermittent fasting
Intermittent fasting has gained significant popularity in recent years as a dietary approach that involves cycling between periods of fasting and eating. While it may seem like a new trend, intermittent fasting has actually been practiced for centuries in various cultures and religions. The primary goal of intermittent fasting is not necessarily to restrict calories, but rather to limit the timespan in which you consume food.
Types of intermittent fasting
There are several different methods of intermittent fasting, each involving different fasting and eating periods. Some of the most common types include:
- 16/8 method: This method involves fasting for 16 hours and limiting the eating window to 8 hours each day. It is often as simple as skipping breakfast and only eating during a specific time period, like between 12 pm and 8 pm.
- 5:2 diet: With this approach, you eat normally for five days of the week and restrict calorie intake to around 500-600 calories for the remaining two days.
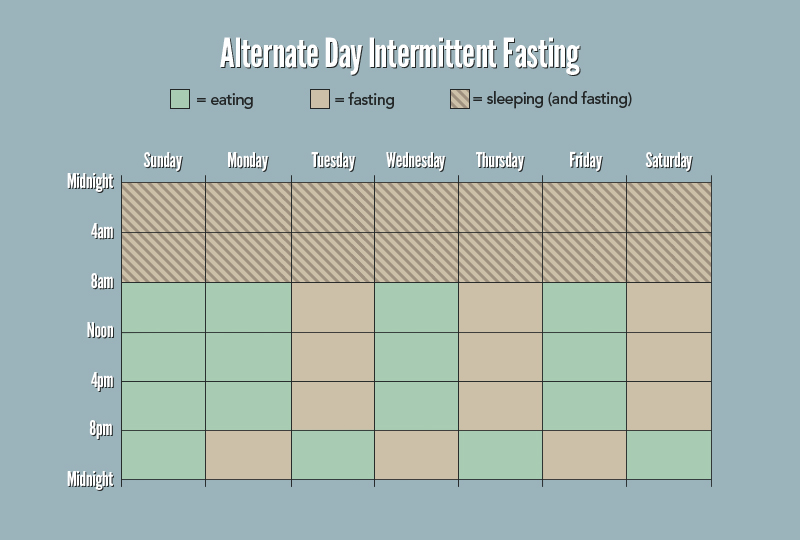
- Alternate-day fasting: As the name suggests, this method involves alternating between fasting days and regular eating days. On fasting days, calorie intake is usually limited to 500-600 calories.
- Eat-stop-eat: This method involves one or two 24-hour fasting periods per week, where no calories are consumed. On regular eating days, you can eat normally.
These are just a few examples, and it’s important to note that there is no one-size-fits-all approach. It’s vital to find a fasting method that suits your lifestyle and health goals.
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Weight loss and improved metabolism
One of the primary motivations for many people to try intermittent fasting is weight loss. By limiting the time window during which you eat, you naturally reduce your caloric intake. This can create a calorie deficit and lead to weight loss. Additionally, intermittent fasting has been observed to increase the levels of human growth hormone (HGH), which can aid in fat burning and muscle gain.
Beyond weight loss, intermittent fasting has also been shown to improve metabolism. It can enhance insulin sensitivity, allowing your body to use glucose more efficiently. This can have a positive impact on blood sugar control, reducing the risk of developing insulin resistance and conditions like type 2 diabetes.
Reduced inflammation and improved brain health
Intermittent fasting has been shown to reduce inflammation in the body, which is associated with numerous chronic diseases. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, intermittent fasting may have a protective effect against conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Furthermore, studies have suggested that intermittent fasting may have cognitive benefits, including improved brain function and protection against neurodegenerative diseases. It is believed that fasting triggers various cellular processes that promote brain health, such as the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports the growth and survival of neurons.
Improved blood sugar control
Intermittent fasting can have a positive impact on blood sugar control and insulin levels. By reducing the frequency of meals, you give your body more time to stabilize blood sugar levels. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance. Several studies have shown that intermittent fasting can lead to significant reductions in fasting blood sugar levels and insulin resistance, thus improving overall metabolic health.
Getting Started with Intermittent Fasting
Consulting with a healthcare professional
Before embarking on any new dietary regimen, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or concerns. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure that intermittent fasting is a suitable approach for you.
Choosing the right fasting schedule
When getting started with intermittent fasting, it is important to choose a fasting schedule that aligns with your lifestyle and preferences. As mentioned earlier, there are several different methods to choose from. Start with an approach that feels manageable and gradually increase the fasting duration as you become more comfortable.
Tips for managing hunger during fasting periods
During fasting periods, it’s natural to experience hunger pangs. Here are some tips to help manage hunger:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water or unsweetened beverages during fasting periods to help curb hunger.
- Consume calorie-free drinks: Coffee, tea, and herbal infusions can help reduce hunger and provide some energy.
- Consume fibrous foods: High-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help keep you feeling fuller for longer.
Remember, it’s normal to feel some discomfort initially as your body adjusts to the fasting routine. Be patient and listen to your body’s needs.
Common Misconceptions about Intermittent Fasting
Fasting doesn’t slow down metabolism
One common misconception about intermittent fasting is that it slows down metabolism. However, research suggests that intermittent fasting does not have a negative impact on metabolic rate. In fact, some studies have shown that it may even increase metabolic efficiency and fat burning.
Not just a trend, but a lifestyle change
Another misconception is that intermittent fasting is just a passing trend. While it has gained popularity in recent years, intermittent fasting is rooted in historical and cultural practices. Moreover, as more research continues to highlight the potential health benefits, it is becoming increasingly recognized as a sustainable lifestyle change rather than a mere fad diet.
Meal Planning for Intermittent Fasting
Choosing nutrient-dense foods
While intermittent fasting primarily focuses on when to eat, it is still important to prioritize nutrient-dense foods during eating windows. Opt for whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients and support overall health.
Creating balanced meals within eating windows
When breaking your fast, aim to create balanced meals that include a variety of food groups. A combination of complex carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats can help ensure you feel satisfied and receive adequate nutrition.
Ensuring hydration during fasting periods
Staying hydrated is crucial during fasting periods. Apart from water, herbal infusions, and unsweetened beverages, you can also include foods with high water content in your meals, such as fruits and vegetables. Proper hydration supports overall health and can help manage hunger during fasting periods.
Exercise and Intermittent Fasting
Timing workouts for optimal results
If you engage in regular exercise, you may wonder how to incorporate it into your fasting routine. It is generally recommended to schedule workouts during the eating window or right before breaking your fast. This allows your body to refuel with necessary nutrients after physical activity.
Addressing concerns about energy levels during fasting
Some individuals may be concerned about experiencing low energy levels during fasting periods. However, many people actually report increased energy and mental clarity while fasting. It may take time for your body to adapt, but as it becomes more efficient at using stored energy, you may experience improved energy levels throughout the day.
Intermittent Fasting and Health Conditions
Safety considerations for individuals with certain health conditions
While intermittent fasting can be beneficial for many individuals, it may not be suitable for everyone. People with certain health conditions, such as eating disorders, diabetes, or low blood pressure, should consult with a healthcare professional before starting intermittent fasting. It’s essential to ensure that this approach aligns with your specific needs.
Potential benefits for conditions like diabetes and heart disease
That being said, intermittent fasting has shown potential benefits for specific health conditions. For instance, research suggests that intermittent fasting can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control, potentially benefiting individuals with diabetes. It may also help reduce the risk factors associated with heart disease, including blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Breaking the Fast: What to Eat
Importance of gradual refeeding
When breaking your fast, it is important to reintroduce food gradually. Avoid consuming large meals immediately after a fast, as this can put a strain on your digestive system. Instead, start with smaller portions and increase gradually over time.
Incorporating whole foods and proteins
Focus on incorporating whole foods and high-quality proteins when breaking your fast. These foods nourish your body and provide essential nutrients after a period of fasting. Including protein-rich foods like lean meats, poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu can help support muscle recovery and overall health.
Avoiding binge-eating behaviors
Intermittent fasting is not an excuse to engage in binge-eating behaviors or overindulge during eating windows. It’s important to approach your meals with mindfulness and listen to your body’s hunger and satiety cues. Be aware of portion sizes and make conscious choices that support your overall well-being.
Intermittent Fasting and Longevity
Exploring the connection between fasting and aging
Interest in the potential link between intermittent fasting and longevity has grown in recent years. Animal studies have shown promising results, suggesting that intermittent fasting may extend lifespan and delay age-related diseases. However, more research is needed to understand the specific mechanisms and implications in humans.
Research on cellular regeneration and disease prevention
Intermittent fasting has also been linked to various cellular regeneration processes. It may promote autophagy, a natural cellular recycling process, and boost the production of antioxidant enzymes. These effects may help protect against diseases and slow down the aging process. Nonetheless, more human studies are necessary to confirm these findings.
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting is a flexible and adaptable dietary approach that offers numerous potential benefits. From weight loss and improved metabolism to reduced inflammation and improved blood sugar control, intermittent fasting has captured the attention of many individuals looking to optimize their health. By consulting with healthcare professionals, choosing the right fasting schedule, and focusing on nutrient-dense foods, you can embark on an intermittent fasting journey that supports your overall well-being. Give it a try and discover the potential benefits for yourself. Cheers to your health and longevity!
Learn about intermittent fasting, a trendy eating pattern that involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. Discover different methods, benefits, and meal planning tips to get started. Improve your overall health and achieve weight loss goals with this flexible way of eating.