The Ketogenic Diet: A Potential Solution for Type 2 Diabetes Management
If you are someone who has been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, you may have heard about the ketogenic diet and its potential benefits. This diet, high in fat and low in carbohydrates, has gained attention for its ability to convert fat into energy instead of sugar, potentially improving blood glucose levels and reducing the need for insulin. However, before embarking on any drastic dietary changes, it is important to consult with your doctor. The ketogenic diet focuses on consuming heart-healthy fats and includes foods such as eggs, fish, avocados, nuts, and seeds. It is crucial to monitor blood glucose and ketone levels while on this diet and work closely with your doctor to make any necessary medication adjustments. Research has shown that the ketogenic diet can lead to improvements in blood sugar control, weight loss, and discontinued insulin requirements for people with type 2 diabetes. While the ketogenic diet offers potential benefits, it is also worth considering other diets, such as a plant-based diet, which may prove to be beneficial for diabetes management as well.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Type 2 Diabetes and Current Management Strategies
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. This resistance leads to an inability of the body to properly regulate blood sugar, resulting in elevated glucose levels. Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease that can lead to serious complications if not managed effectively.
Common management strategies for type 2 diabetes
The management of type 2 diabetes typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and increased physical activity, as well as medication. The main goal is to control blood sugar levels and prevent further complications. Common strategies include monitoring blood glucose levels, following a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, taking prescribed medications, and managing stress levels. These strategies are aimed at improving insulin sensitivity, promoting weight loss, and maintaining overall health.
Limitations of current management strategies
While current management strategies for type 2 diabetes are effective for many individuals, there are limitations to their success. Some individuals may struggle to achieve and maintain optimal blood sugar control, despite adhering to recommended lifestyle modifications and taking prescribed medications. Additionally, some individuals may experience unwanted side effects from certain medications. In light of these limitations, alternative approaches to diabetes management, such as the ketogenic diet, have gained attention.
Introduction to the Ketogenic Diet
What is the ketogenic diet?
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that has gained popularity in recent years for its potential health benefits. It involves drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and replacing it with healthy fats. The reduced carbohydrate intake forces the body to switch its primary source of fuel from glucose to ketones, which are produced by the liver from stored fat. This metabolic state is known as ketosis.
Principles of the ketogenic diet
The main principle of the ketogenic diet is to restrict carbohydrate intake to a level that triggers ketosis. Typically, carbohydrate intake is limited to around 20-50 grams per day. This allows the body to rely on fat for energy instead of glucose. The diet focuses on consuming high-quality fats, moderate amounts of protein, and very low amounts of carbohydrates. Examples of foods commonly consumed on the ketogenic diet include eggs, fish, avocados, nuts, and seeds. It is important to note that the ketogenic diet is a highly individualized approach, and macronutrient ratios may vary depending on an individual’s specific needs and preferences.
How does the ketogenic diet work for type 2 diabetes?
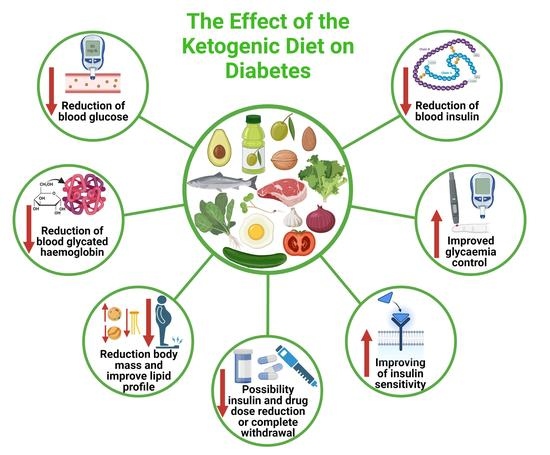
The ketogenic diet has been found to be beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes due to its ability to improve blood sugar control and reduce insulin resistance. By significantly reducing carbohydrate intake, the production and release of glucose from dietary sources are limited, which in turn leads to lower blood sugar levels. Additionally, in a state of ketosis, the body becomes more efficient at utilizing stored fat for energy, which can lead to weight loss. Losing excess weight can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the need for exogenous insulin. The ketogenic diet also has anti-inflammatory properties, which may further contribute to its positive effects on blood sugar control.
Key benefits of the ketogenic diet for type 2 diabetes
Numerous studies have demonstrated the potential benefits of the ketogenic diet for people with type 2 diabetes. One of the key benefits is improved blood sugar control. Research has shown that the ketogenic diet can lead to significant reductions in HbA1c levels, a marker of long-term blood sugar control. Additionally, the diet has been associated with decreased fasting blood glucose levels and improved insulin sensitivity. Moreover, the ketogenic diet has been shown to promote weight loss, which can lead to additional improvements in blood sugar control and overall metabolic health. These benefits make the ketogenic diet an attractive option for individuals with type 2 diabetes who are looking for alternative approaches to managing their condition.
Scientific Evidence Supporting the Ketogenic Diet for Type 2 Diabetes
Studies demonstrating improvements in blood sugar control
Several studies have shown that the ketogenic diet can result in significant improvements in blood sugar control for people with type 2 diabetes. In a study published in the journal Nutrition & Metabolism, researchers found that after 12 weeks of following a ketogenic diet, participants experienced a 16% reduction in fasting blood glucose levels and a 37% decrease in HbA1c levels. Another study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research found that participants who followed a very low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet for 10 weeks experienced a significant decrease in HbA1c levels compared to a control group that followed a standard low-fat diet.
Research on weight loss and the ketogenic diet
Weight loss has been shown to have a positive impact on blood sugar control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. The ketogenic diet has been found to be an effective tool for weight loss due to its ability to suppress appetite, increase satiety, and reduce overall calorie intake. In a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, researchers compared the effects of a low-fat diet and a low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet on weight loss. They found that participants on the ketogenic diet lost more weight, including a larger reduction in visceral fat (fat stored around the organs), compared to those on the low-fat diet. This weight loss may translate into improved blood sugar control and reduced insulin requirements for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Effectiveness of the ketogenic diet in reducing insulin requirements
Reducing the need for exogenous insulin is a major goal in the management of type 2 diabetes. The ketogenic diet has shown promise in this regard. A study published in the journal Nutrition & Diabetes examined the effects of a very low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet on insulin usage in individuals with type 2 diabetes. The researchers found that participants experienced a 72% decrease in insulin requirements after 12 weeks on the diet. This reduction in insulin usage suggests that the ketogenic diet may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the reliance on exogenous insulin.
Important Considerations Before Starting the Ketogenic Diet
Consulting with a healthcare professional
Before embarking on any new dietary approach, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes. A healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or a diabetes specialist, can provide personalized guidance and ensure that the ketogenic diet is suitable for your individual needs and health status. They can help assess any potential risks or contraindications, monitor progress, and make necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
Monitoring blood glucose and ketone levels
When following a ketogenic diet, it is essential to regularly monitor both blood glucose and ketone levels. Blood glucose monitoring helps ensure that blood sugar levels are within the target range and enables adjustments to food choices and insulin dosages if necessary. Ketone monitoring is important to ensure that the body is in a state of ketosis, as this is crucial for the therapeutic effects of the ketogenic diet. Home ketone testing kits are available for this purpose.
Making necessary medication adjustments
As the ketogenic diet can have a significant impact on blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to adjust any diabetes medications accordingly. Medication adjustments may be necessary to prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and ensure optimal blood sugar control. It is vital to follow the guidance and recommendations of a healthcare professional when making changes to medication regimens.
Implementing the Ketogenic Diet for Type 2 Diabetes Management
Dietary recommendations for the ketogenic diet
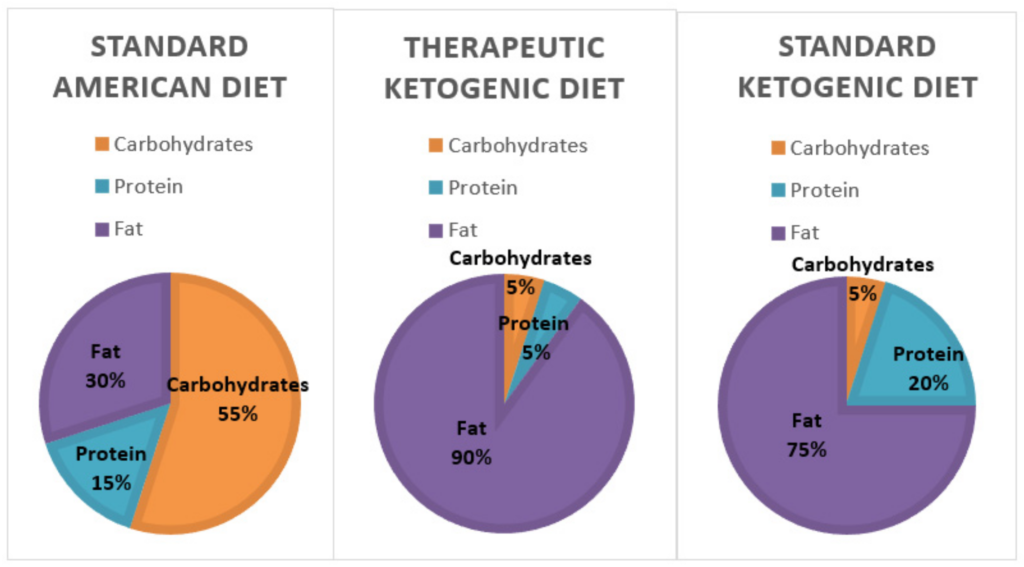
The ketogenic diet is characterized by high fat, moderate protein, and very low carbohydrate intake. As a general guideline, the macronutrient breakdown of the ketogenic diet is approximately 70-75% fat, 20-25% protein, and 5-10% carbohydrates. However, individualized recommendations may vary depending on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and specific health needs. It is important to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to tailor your macronutrient ratios to meet your specific requirements.
Foods to include in the ketogenic diet
The ketogenic diet focuses on consuming healthy fats, moderate amounts of protein, and minimal carbohydrates. Foods that are typically included in the ketogenic diet include:
- Healthy fats: Avocados, coconut oil, olive oil, nuts, and seeds.
- Protein sources: Eggs, fish, poultry, lean meats, and plant-based protein sources such as tofu and tempeh.
- Low-carbohydrate vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, and bell peppers.
- Limited carbohydrates: Berries in moderation, small amounts of low-carbohydrate fruits such as avocado and tomatoes.
It is important to avoid foods high in refined carbohydrates and sugars, such as sugary beverages, sweets, grains, and processed foods.
Meal planning and preparation tips
Meal planning and preparation are key to successfully implementing the ketogenic diet. Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Plan your meals in advance: Plan out your meals for the week, including snacks, and create a shopping list based on your meal plan.
- Meal prep: Prepare meals and snacks in advance to make it easier to stick to your dietary goals, especially during busy days.
- Experiment with recipes: Explore and try new recipes that adhere to the principles of the ketogenic diet. There are numerous resources available online for keto-friendly recipes and meal ideas.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support overall health and wellbeing.
Potential challenges and strategies for overcoming them
Implementing the ketogenic diet for type 2 diabetes management can come with its challenges. Some potential challenges may include:
- The initial adjustment period: The transition from a high-carbohydrate diet to a low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet can be challenging initially. It is common to experience symptoms such as fatigue, irritability, and decreased physical performance during the adaptation phase. These symptoms typically resolve within a week or two as the body adjusts to utilizing fats and ketones for energy.
- Social situations and dining out: Social situations and dining out can present challenges when following a specific dietary plan. It may require some planning and communication to ensure that suitable food options are available. It can be helpful to look for ketogenic-friendly restaurants or choose menu items that align with the principles of the diet.
- Monitoring nutrient intake: With the restrictive nature of the ketogenic diet, it is essential to pay attention to nutrient intake and ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs. This may require the use of supplements or incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your meals.
By being aware of these potential challenges and utilizing strategies to overcome them, individuals with type 2 diabetes can successfully implement the ketogenic diet as part of their diabetes management plan.
Other Dietary Approaches for Type 2 Diabetes Management
The plant-based diet and its potential benefits for type 2 diabetes
Another dietary approach that has shown promise for type 2 diabetes management is the plant-based diet. This diet focuses on consuming primarily plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, while minimizing or excluding animal products. Numerous studies have demonstrated the potential benefits of a plant-based diet for type 2 diabetes, including improvements in blood sugar control, weight loss, and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. The plant-based diet can be tailored to individual preferences and can still include some animal products if desired.
Comparing the effectiveness of the ketogenic diet and plant-based diet
Both the ketogenic diet and plant-based diet have shown promise in managing type 2 diabetes. While the ketogenic diet focuses on low carbohydrate and high-fat intake, the plant-based diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed plant foods and limits or excludes animal products. The choice between these two diets ultimately depends on individual preferences, goals, and health status. Some individuals may find success with one approach, while others may prefer or respond better to the other. It is important to consider personal needs, dietary preferences, and work with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable dietary approach for type 2 diabetes management.
Case Studies and Personal Experiences
Success stories of individuals with type 2 diabetes using the ketogenic diet
There have been numerous success stories of individuals with type 2 diabetes who have experienced positive outcomes by following the ketogenic diet. These success stories often highlight significant improvements in blood sugar control, weight loss, and decreased reliance on medication. Personal testimonials demonstrate the potential benefits of the ketogenic diet for managing type 2 diabetes and provide motivation and inspiration for others considering this dietary approach.
Challenges faced and strategies for maintaining the diet long-term
While the ketogenic diet can be effective for type 2 diabetes management, it is not without its challenges. Some individuals may find it difficult to adhere to the dietary restrictions and macronutrient ratios long-term. Strategies for maintaining the diet include:
- Seeking support: Joining support groups, finding an accountability partner, or working with a registered dietitian who specializes in the ketogenic diet can provide guidance and support.
- Incorporating variety: Ensuring a wide variety of foods within the parameters of the diet can help prevent boredom and make the diet more sustainable.
- Flexibility: Being flexible with the diet when necessary, considering individual preferences and occasional indulgences, can help maintain long-term compliance.
- Focus on overall health: Remembering that the ketogenic diet is just one aspect of a healthy lifestyle can help maintain focus and motivation. Incorporating regular physical activity, managing stress, and prioritizing overall self-care are also important components of successful long-term diabetes management.
Potential Risks and Limitations of the Ketogenic Diet for Type 2 Diabetes
Possible side effects and risks of the ketogenic diet
While the ketogenic diet can have significant benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes, it is important to be aware of potential side effects and risks. Some potential side effects of the ketogenic diet can include:
- The “keto flu”: During the initial stages of transitioning to a ketogenic diet, some individuals may experience symptoms such as fatigue, headache, dizziness, and nausea. These symptoms are often temporary and resolve within a week or two as the body adapts to using ketones for energy.
- Nutritional deficiencies: The restrictive nature of the ketogenic diet can lead to deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It is important to ensure adequate intake of nutrient-dense foods and consider appropriate supplementation if needed.
- Increased risk of hyperlipidemia: The high fat content of the ketogenic diet, particularly saturated fats, can lead to elevated cholesterol levels in some individuals. Monitoring lipid profiles and adjusting fat intake may be necessary for those at higher risk of cardiovascular disease.
Individual variations and responses to the diet
As with any dietary approach, individual responses to the ketogenic diet can vary. It is important to monitor blood glucose levels, ketone levels, and overall health markers to assess how the diet is affecting your body. Some individuals may find that the ketogenic diet is not suitable for them or may experience minimal benefits. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional to interpret and evaluate individual responses to the diet and make any necessary adjustments to optimize diabetes management.
Long-term sustainability of the ketogenic diet
The long-term sustainability of the ketogenic diet for type 2 diabetes management is a topic of ongoing research and discussion. While it can be effective in the short term, questions remain about its feasibility and sustainability over a lifetime. The restrictive nature of the diet can be challenging to maintain indefinitely and may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, the potential risks and limitations associated with the ketogenic diet should be carefully considered. It is essential to evaluate the individual’s goals, preferences, and health status on an ongoing basis and work with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate long-term dietary approach for type 2 diabetes management.
In conclusion, the ketogenic diet has shown promise as an alternative approach to managing type 2 diabetes. It offers potential benefits such as improved blood sugar control, weight loss, and reduced insulin requirements. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any drastic dietary changes. Monitoring blood glucose and ketone levels, adjusting medications as needed, and ensuring individualized recommendations are followed are crucial components of successful implementation. While the ketogenic diet is one option for type 2 diabetes management, other dietary approaches, such as the plant-based diet, may also be beneficial. The choice of diet ultimately depends on individual preferences, health status, and goals. By working closely with a healthcare professional, individuals with type 2 diabetes can find the most suitable dietary approach for their personal needs and effectively manage their condition.
Discover the potential benefits of the ketogenic diet for managing type 2 diabetes. Learn how it improves blood sugar control, promotes weight loss, and reduces insulin requirements. Consult with your doctor before making any dietary changes.